MPLS Network Pros and Cons: Factors to Weigh for Your Global Business

Many global organizations are faced with the decision of whether to move away from MPLS in favor of other alternatives. Unfortunately, there’s no one size fits all solution to this question. The answer largely depends on the organization’s goals and the current state of the nation.
When MPLS entered the market in the 90s, many CIOs and IT professionals who saw it was a pathway to drive growth in the burgeoning digital age. However, the technologies that MPLS supported eventually began to outgrow the network that housed them, and MPLS has been struggling to keep up ever since.
Those same organizations that welcomed MPLS two decades ago are now wrestling with the decision of whether to keep it or change to a solution that can accommodate cloud applications and remote teams.
Even those solutions are not always cut and dry. VPNs can now be delivered as a software overlay that does not require specialized MPLS hardware or services. MPLS may still hold some advantages for enterprises that would like to maintain a hybrid WAN environment.
So, what’s an organization to do? Like any good business decision, the choice about whether to stick with MPLS or explore other options should come only after weighing the advantages and disadvantages of MPLS with other network options against goals and other constraints.
Only the organization itself can make the final decisions, but this list of MPLS pros and cons can help plant the seeds for further discussion:
MPLS Advantages & Benefits
Here are a few of the reasons why it might make sense for an organization to keep or adopt an MPLS network solution:
- It’s a reliable technology that has served enterprises for years with direct routes from one edge to another.
- It’s a quality connection that offers a consistent user experience with no packet loss, fixed latency, and low jitter.
- It’s the safe bet for organizations that are averse to change and do not require higher-level functionality
MPLS Disadvantages
On the flip side, here are a few of the drawback associated with MPLS:
- It’s optimized for point-to-point connectivity and not point to cloud, meaning there is no way to directly access every cloud or SaaS application with MPLS. Only 2% of cloud services provide this access and with a significant premium
- It requires WAN optimization to streamline the delivery, which adds extra cost on top of a solution that can already be pricey.
- It takes a long time to deploy, especially when office locations are spread across different states or countries. It can take up to 6-8 months to get each new site up and running
- The cost is high because of limited competition in the marketplace
MPLS vs SD WAN: Weighing the Options for an Enterprise
Considering the pros and cons of MPLS is a first step in determining the right network solution for an enterprise, but it should not be the only step in the process.
Changing a network is a big investment and not a decision that should be taken lightly. The choice an organization makes will be in place for years to come, if not even longer than that.
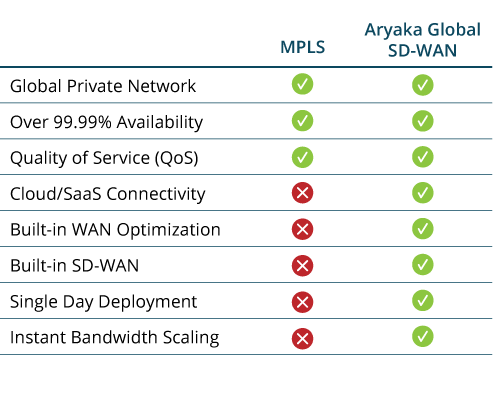
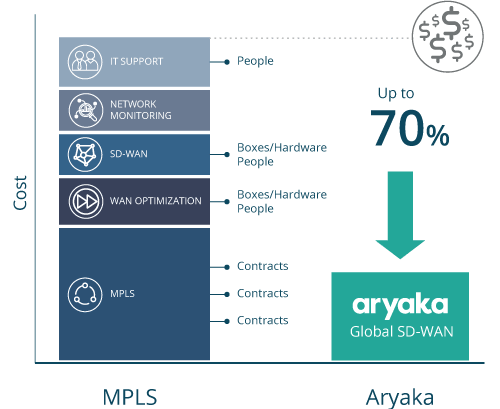
Read Aryaka’s white paper on key considerations for MPLS vs. SD-WAN for more information all of the factors an organization should consider when deciding on the best network solution for their current and future needs.
- Is MPLS dead? Understanding Need For mpls Network Technology
- What is MPLS network & How MPLS Works?
- 4 Reasons Why MPLS No Longer Serves Global Enterprises
- MPLS Network Pros and Cons
- SDWAN over MPLS: Is SD-WAN Better than MPLS?
- 5 Questions MPLS Providers Hope You Won’t Ask
- 3 Simple Ways for Choosing the Right MPLS Alternative
- The Slow Death of MPLS
- Can a Global SD-WAN Replace MPLS Connectivity?



